introduction
Organic chemistry is full of mysterious-looking formulas that appear confusing at first glance. A combination like HCOOCH + CH₂ + H₂O may not look familiar to the average person, yet it represents real elements of organic and biochemical reactions. To understand it properly, we need to explore the individual parts of the formula, how they behave chemically, and where such compounds exist in daily life, industry, and the environment.
This article breaks down:
- The meaning of HCOOCH
- The structure and significance of CH₂
- The reaction involving H₂O (water)
- Practical examples involving ester hydrolysis, alcohol formation, hydrocarbons, and industrial chemistry
- Where these types of molecules appear in biology, food, fuels, and materials
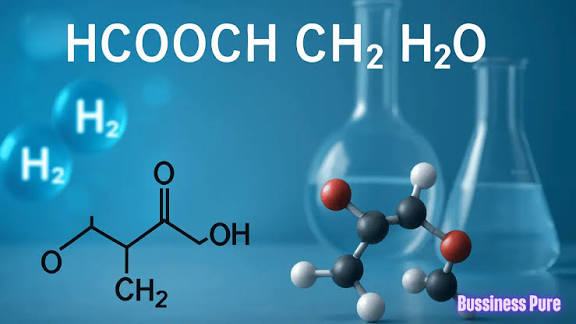
1. What is HCOOCH?
The formula HCOOCH closely resembles part of a formate ester. Formate esters are organic compounds derived from formic acid (HCOOH) and alcohols.
Examples include:
- Methyl formate – HCOOCH₃
- Ethyl formate – HCOOC₂H₅
Formate esters are important in:
| Usage | Examples |
|---|---|
| Industrial solvents | Methyl formate is used in resins, adhesives, cleaning agents |
| Perfumes & foods | Ethyl formate gives fruity smells like rum, strawberries, and raspberries |
| Pharmaceuticals | Used in production of certain medicines |
So, when we see HCOOCH, it usually represents part of an ester molecule. To complete the structure, it must bond with at least one more atom (like H, CH₃, C₂H₅, etc.).
2. What does CH₂ mean?
CH₂ is the building block of hydrocarbons, forming the backbone of many organic chemicals.
It is present in:
| Type of Compound | Example |
|---|---|
| Alkanes | Propane (C₃H₈), Butane (C₄H₁₀) |
| Alkenes | Ethene (C₂H₄), Propene (C₃H₆) |
| Polymers | Polyethylene (—CH₂—CH₂—)ₙ |
CH₂ is extremely important because:
- It forms long carbon chains (fossil fuels, plastics)
- It reacts with other chemicals to create alcohols, aldehydes, esters, and acids
- It appears in biochemical pathways inside living organisms
When combined with esters or water, CH₂ participates in hydrolysis, combustion, and polymerization processes.
3. Where does H₂O fit in?
Water is one of the most important reactants in organic chemistry. It participates in:
Hydrolysis – breaking molecules apart
Hydration – adding water to hydrocarbons
Biochemical metabolism
Industrial chemical reactions
When organic molecules like esters react with water, a process called hydrolysis occurs.
4. Putting it Together: HCOOCH + H₂O → Hydrolysis Reaction
If we interpret the original formula as involving hydrolysis, the reaction looks like this:
Formate Ester + Water → Formic Acid + Alcohol
General reaction:HCOOR+H2O→HCOOH+ROHHCOOR + H₂O → HCOOH + ROHHCOOR+H2O→HCOOH+ROH
Where:
- HCOOR = formate ester
- HCOOH = formic acid
- ROH = alcohol
Example:
Methyl Formate + Water → Formic Acid + MethanolHCOOCH3+H2O→HCOOH+CH3OHHCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OHHCOOCH3+H2O→HCOOH+CH3OH
This is a common industrial reaction.
5. Role of CH₂ in These Reactions
CH₂ is found in many alcohols formed from hydrolysis.
Examples:
- Ethyl formate → Ethanol (contains CH₂CH₃)
- Propyl formate → Propanol (contains CH₂CH₂CH₃)
When an ester with CH₂ reacts with water:HCOO−CH2R+H2O→HCOOH+HO−CH2RHCOO-CH₂R + H₂O → HCOOH + HO-CH₂RHCOO−CH2R+H2O→HCOOH+HO−CH2R
So CH₂ often ends up inside the alcohol product.
This process is used in:
- Alcohol manufacturing
- Perfume industries
- Pharmaceutical chemicals
- Biofuel conversion
6. Real-World Importance of Molecules Like HCOOCH and CH₂
A. Food and Flavors
Ethyl formate gives fruity smell and taste:
- Strawberries
- Rum
- Raspberries
- Certain soft drinks and candies
Many artificial fruit flavors depend on formate esters.
B. Perfume Industry
Esters are responsible for sweet, floral, and fruity fragrances. Hydrolysis helps separate or refine oils in perfume production.
C. Fuels and Biofuels
CH₂ units form long hydrocarbon chains found in:
- Gasoline
- Diesel
- Natural gas
- LPG
- Jet fuel
Hydrolysis and catalytic processes convert biomass into usable fuels.
D. Polymers and Plastics
CH₂ is essential in polymer chemistry:
- Polyethylene (shopping bags, bottles)
- PVC
- Synthetic rubbers
CH₂ repeating units form strong, flexible materials.
E. Pharmaceuticals
Formate chemistry is used to create:
- Pain relievers
- Antibiotics
- Anesthetics
- Antiseptics
Hydrolysis and esterification reactions are part of drug synthesis.
7. Biological Significance
These molecules also matter inside living organisms.
Formic Acid (HCOOH)
- Produced by ants and bees
- Used by insects as defense mechanism
- Can appear in human metabolism during methanol poisoning
Alcohols with CH₂ groups
- Ethanol (in alcoholic drinks)
- Propanol and butanol (used in medicines, disinfectants)
- Sugars contain repeating CH₂ units
Water (H₂O) drives most reactions inside cells.
8. Hydration of CH₂ in Alkenes
Another way to interpret CH₂ + H₂O is:CH2=CH2+H2O→CH3CH2OHCH₂=CH₂ + H₂O → CH₃CH₂OHCH2=CH2+H2O→CH3CH2OH
This is the production of ethanol from ethene.
- Used in fuel
- Used in medicine
- Used in beverages
- Used in sanitizers
This reaction is extremely common in chemical plants.
9. Environmental and Industrial Perspective
Benefits
- Helps produce eco-friendly solvents
- Used in biodegradable ester products
- Important in green chemistry and biofuel production
Pollution Considerations
- Hydration and hydrolysis reactions can produce toxic alcohols if mishandled
- Industrial effluents must be treated
- Safer alternatives like bio-esters are being developed
Many industries now use renewable sources such as sugarcane, plants, and organic waste to create formate esters and alcohols.
10. Final Summary
Although HCOOCH + CH₂ + H₂O looks simple, it represents a powerful section of organic chemistry. It outlines the relationship between esters, hydrocarbons, and water—a combination that leads to important products:
formic acid
industrial alcohols
fragrances and flavors
fuels
polymers
medicines
These reactions connect chemistry with everyday human life—from fuel in cars to perfumes, fruit flavors, hand sanitizers, and plastic products.
Conclusion
Understanding even small chemical formulas opens the door to entire industries, biological processes, and environmental science. HCOOCH, CH₂, and H₂O are not random symbols—they are the foundation of reactions that shape modern chemistry, technology, and daily human life.